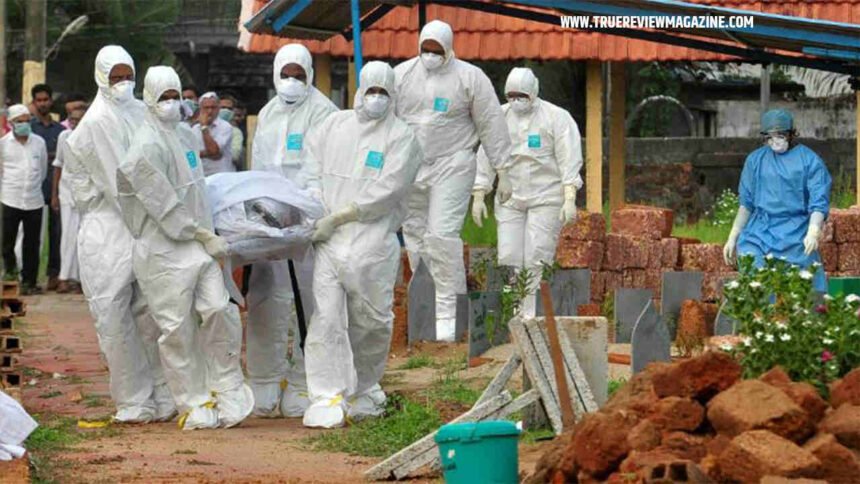
In southern India, a state has initiated measures to combat an outbreak of the Nipah virus following the unfortunate deaths of two individuals due to this rare and potentially lethal disease. These actions involve the temporary closure of schools and the implementation of extensive testing protocols to curtail any further spread.
Pinarayi Vijayan, Kerala’s Chief Minister, officially confirmed the virus’s presence in the Kozhikode district and urged residents to exercise vigilance while adhering to the health department’s recommendations. Remarkably, this marks the fourth occurrence of a Nipah virus outbreak in the state since 2018. In his statement, Vijayan sought to reassure the public, emphasizing the importance of addressing the situation with caution rather than fear.

The Nipah virus is categorized as a zoonotic virus, capable of transmission from animals to humans. Additionally, it can spread through contaminated food or direct human-to-human contact. Infection with the virus can lead to a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild to severe. Initial manifestations typically include headaches and drowsiness, which can rapidly progress to a coma within a matter of days. Moreover, the virus has the potential to induce acute respiratory syndrome and fatal encephalitis, characterized by brain inflammation. Regrettably, there is no vaccine available at present, and treatment options are confined to supportive care.
In response to the outbreak in Kerala, health authorities have undertaken an extensive contact-tracing effort, identifying over 700 individuals with close contact with the affected cases. Among this group, 77 individuals are classified as “high risk” and have been advised to self-isolate while diligently monitoring their health.

To contain the outbreak, officials in Kozhikode have implemented school closures, and seven villages have been designated as “containment zones.”
This recent incident is not the first time Kerala has grappled with the Nipah virus. In 2018, the state confronted a devastating outbreak that claimed the lives of 17 people, generating widespread panic. During that critical period, meticulous contact tracing and rigorous testing were instrumental in containing the virus’s spread, even though healthcare workers were not spared from contracting the disease.
The subsequent year, Kerala initiated surveillance measures involving more than 300 individuals following the diagnosis of a Nipah virus case. In 2021, yet another outbreak occurred, tragically resulting in the loss of a 12-year-old boy’s life.
The Nipah virus initially gained notoriety during a 1998-1999 outbreak in Malaysia, where it infected nearly 300 individuals and led to the unfortunate demise of over 100 people. In a bid to halt its dissemination, a substantial culling of pigs was carried out during that period. The virus was christened after the Malaysian village of Kampung Sungai Nipah, where pig farmers contracted the illness.
Historically, most instances of human infections were linked to direct contact with sick pigs or their contaminated tissues. Nevertheless, there have been documented cases of human-to-human transmission, notably among healthcare personnel providing care to infected patients. Due to its epidemic potential, the Nipah virus is categorized as an urgent priority for research and development by the World Health Organization (WHO).
In response to the present outbreak, Indian authorities have embarked on a concerted effort to contain the virus, safeguard public health, and avert any further harm.
In Short
the diligent efforts of Indian authorities in response to the Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala highlight the importance of swift action and public awareness in facing health crises. By staying informed and following recommended guidelines, we can collectively mitigate the impact of such outbreaks, ensuring the safety and well-being of our communities. Let this be a reminder of the significance of preparedness and vigilance in safeguarding public health.
In southern India, authorities are swiftly addressing a Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala. This blog explores the outbreak’s background, the state’s response, and its implications, providing a comprehensive overview of the situation.
Click here : https://truereviewmagazine.com/










